
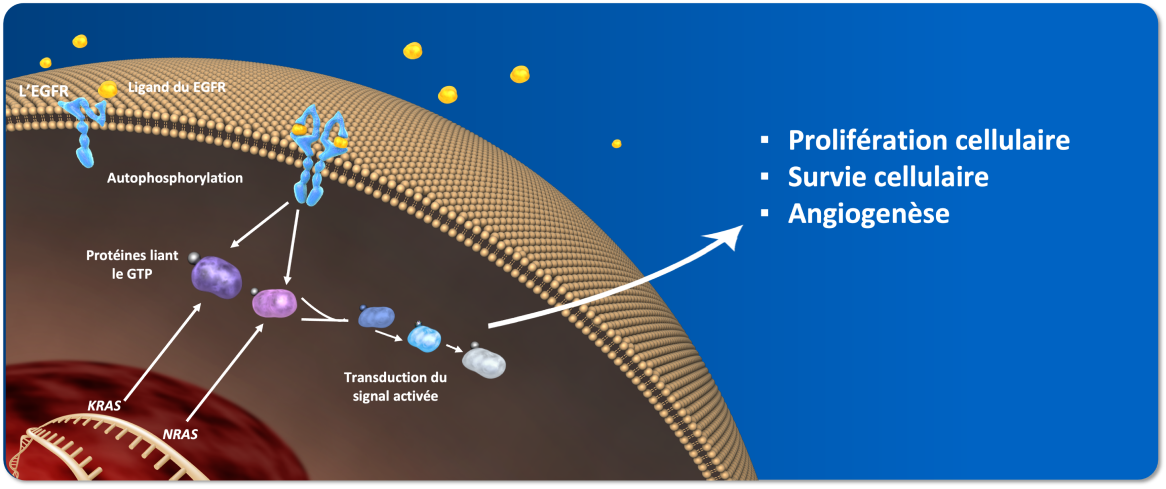
Les ligands de l’EGFR se lient au récepteur et activent la signalisation de l’EGFR en induisant l’autophosphorylation du récepteur1.
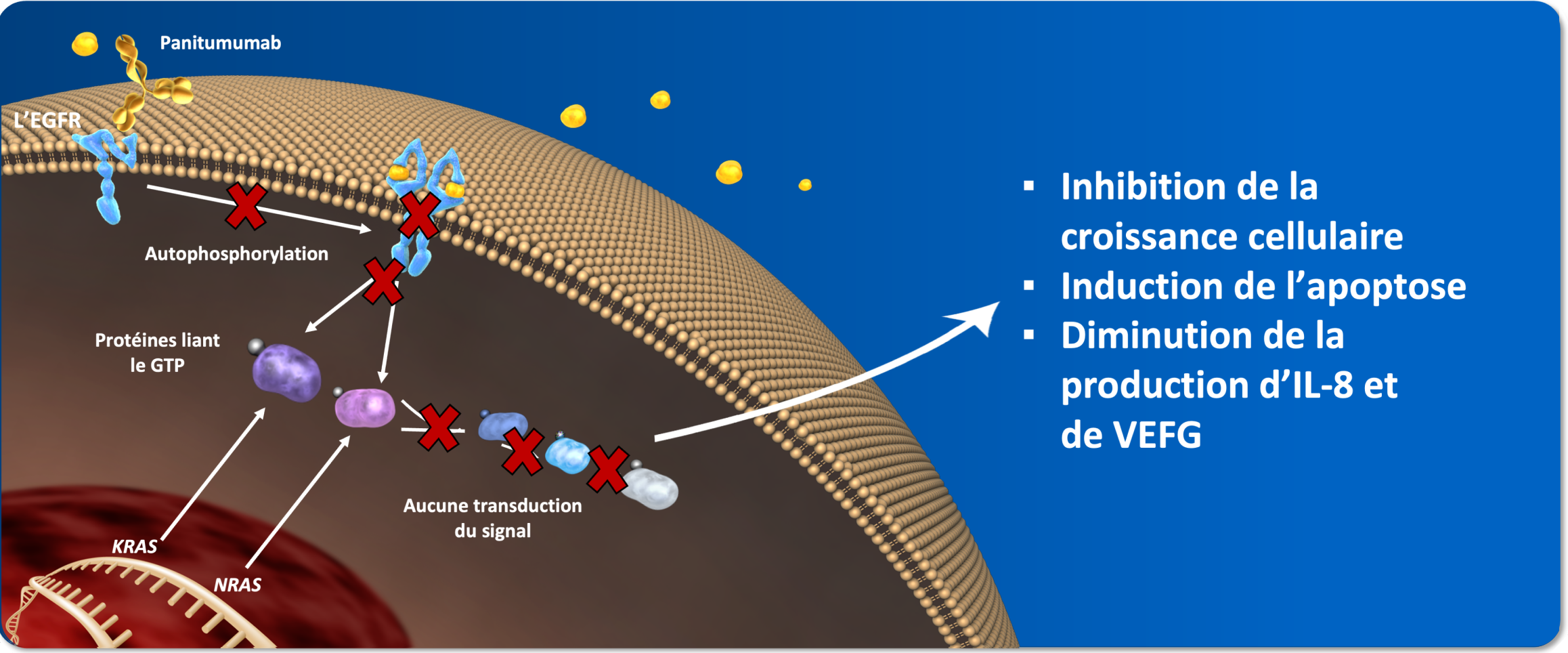
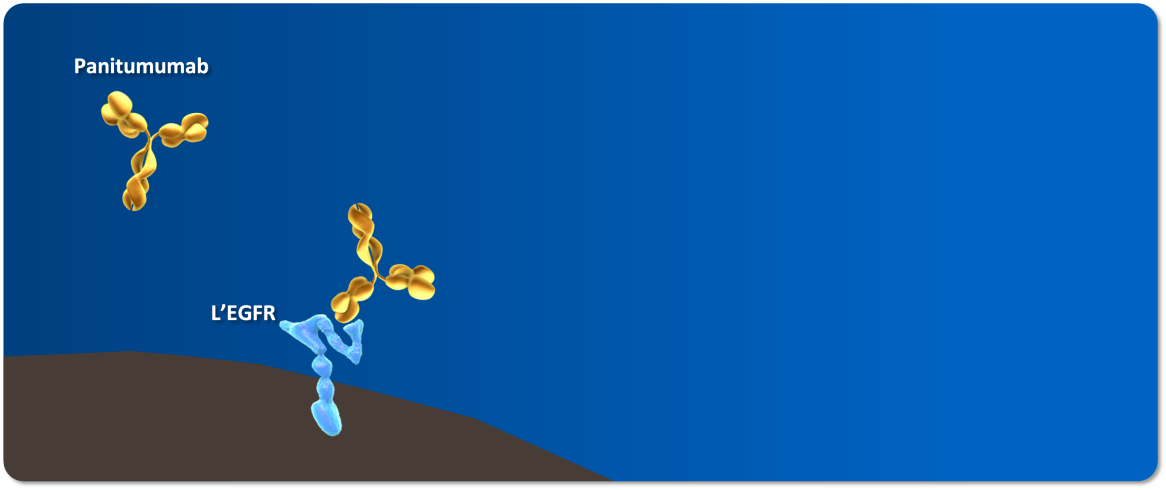
Le panitumumab se lie au domaine de liaison du ligand de l’EGFR et inhibe de manière compétitive l’autophosphorylation du récepteur induite par tous les ligands connus de l’EGFR1.
D’après la monographie du Vectibix1.
